Announcements, Azure Blob Storage, Azure SQL Database, Databases, Storage
Adaptive caching powers Azure SQL Data Warehouse performance gains
Posted on
3 min read
Today we made Azure SQL Data Warehouse (SQL DW) Compute Optimized Gen2 Tier generally available to our customers. Even though data and data sources grow exponentially, organizations continue to demand faster and faster insights. Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier delivers on this need with major performance improvements made possible through adaptive caching.
Analytics workload performance is typically determined by two major factors, I/O bandwidth to storage and repartitioning speed, also known as shuffle speed. This blog post looks under the hood of how Azure SQL DW exploits the latest hardware trends to improve effective I/O bandwidth available.
One of the recent hardware innovations becoming widely available are NVM Express (NVMe) solid-state drive (SSD) devices. NVMe SSDs offer significantly more I/O bandwidth than SATA SSDs or hard drives. A typical single NVMe device used in Azure, generally offers up to 2GB/sec of local I/O bandwidth, with multiple devices available per physical host, resulting in bandwidth previously reserved only to very high-end storage systems. Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier fully takes advantage of NVMe devices through adaptive caching of recently used data on NVMe. With this breakthrough on customer workloads, we have observed up to five times the improvement in query performance, compared with the first generation of Azure SQL DW and some workloads improved even more.
“After upgrading to the Gen2 of Azure SQL Data Warehouse, our data warehouse workload has seen an average of 4 times performance improvement. We have been working with Azure SQL Data Warehouse Compute Optimized Gen2 tier since its inception and the use of NVMe SSDs have shown the largest performance improvement we have seen to the service” said Rajeev Acharya, Senior Software Engineer at the Windows Data and Analytics (DnA) team for Microsoft.
Before we delve into details, I’d like to describe on how SQL Server implements industry leading columnar storage, which is the default storage type used in Azure SQL DW. Columnstore divides table rows into 1 million row units called rowgroups and compresses each column within the row group. A variety of compression techniques are used, such as dictionaries, bit-packing, and run-length encoding. When data is scanned, only required columns are read into memory. Compression and columnar oriented storage results in significant reduction of I/O requirements. In addition, in many cases SQL Server engine operates directly over compressed data, taking full advantage of vectorized CPU extensions such as AVX. The combination of both techniques often results in up to 10 times the improvement in query speeds over row-stores.
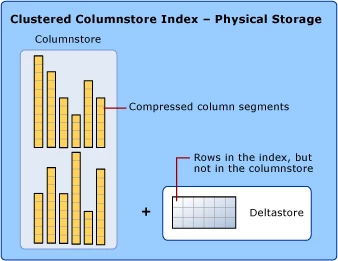
Using column stores does not require the applications to remove updates or deletes, those are tracked into delta store tables and once enough changes happen, the data is recompressed back into the column store representation. You can find a more detailed description of SQL Server column stores.
Azure SQL DW is comprised of multiple compute nodes, each running an instance of SQL Server engine and a Data Movement Service (DMS) which is responsible for data repartitioning operations. SQL DW decouples compute from storage – both can scale independently, and the data warehouse instance can be paused while keeping all the data resident in Azure storage. This gives our customer flexibility to build a cloud data warehouse solution, for their unique needs, and scale up and down easily, truly leveraging the elasticity of cloud computing.
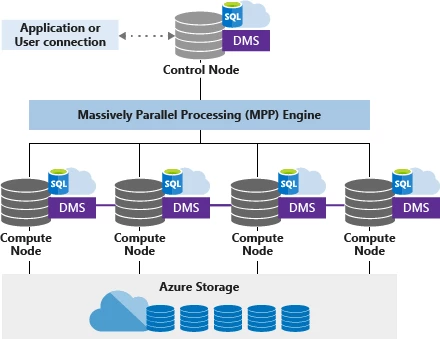
For Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier, each compute node runs on NVMe based node. Each SQL DW compute node maintains a cache of recently accessed SQL Server columnar storage segments, optimized for local access and available via network to other Azure SQL DW nodes as needed. Because the SQL DW cache tracks columnar segments, only frequently accessed tables, rowgroups and columns end up being cached at the correct granularity.
SQL DW columnar cache is a built-in feature for Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier, no additional set up or configuration is required. For example, we have optimized the cache to work well with occasional large queries which may access more data than local NVMe storage capacity available to Azure SQL DW instance. The columnar storage cache is also resilient to failures, so a failure of SQL DW node will not result in loss of performance for the cached data, and additional copies of cached data get created as needed.
Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier blends fast local performance enabled by NVMe devices with elasticity only possible in cloud. The presence of adaptive caching continues to allow the data warehouse instance to be resized or paused to save our customer money. When an SQL DW instance is resumed after a pause, SQL DW populates cache again from Azure Storage as data is queried.
You can now learn more about: