An experimentation platform for improving app resilience
Improve application resilience with chaos engineering and testing by deliberately introducing faults that simulate real-world outages. Azure Chaos Studio is a fully managed chaos engineering experimentation platform for accelerating discovery of hard-to-find problems, from late-stage development through production. Disrupt your apps intentionally to identify gaps and plan mitigations before your customers are impacted by a problem.
Explore the benefits of Azure Chaos Studio
Subject your Azure applications to real or simulated faults
Observe how your applications respond to real-world disruptions
Integrate chaos engineering experiments into any phase of quality validation
Use the same tools as Microsoft engineers to build resilience of cloud services

Improve the reliability of your Azure applications
Experiment by subjecting your Azure apps to real or simulated faults in a controlled manner to better understand application resilience. Observe how your apps will respond to real-world disruptions such as network latency, an unexpected storage outage, expiring secrets, or even a full datacenter outage with chaos engineering and testing.

Experiment on your own terms
Validate product quality when and where it makes sense for your organization. Take advantage of a hypothesis-based approach to drive application resilience with integrated chaos in your CI/CD pipeline, through drill events, game days, or a combination of both. Use the continuously growing fault library to validate your architecture, configuration, code, monitoring, and the staffing and resources you need to be more resilient.
Gain insights without the chaos of getting started
Avoid the need to manage tools and scripts while spending more time learning about your application's resilience. Get started quickly with experiment templates and an expanding library of faults—including agent-based faults that disrupt within resources and service-based faults that disrupt resources at the control plane.


Go beyond fault injection with reliability validation
Improve application reliability by implementing a cohesive strategy to make informed decisions before, during, and after chaos experiments. Integrate load testing into your chaos experiments to simulate real-world customer traffic. Disrupt your apps intentionally to identify gaps and plan mitigations before your customers are impacted by a problem.
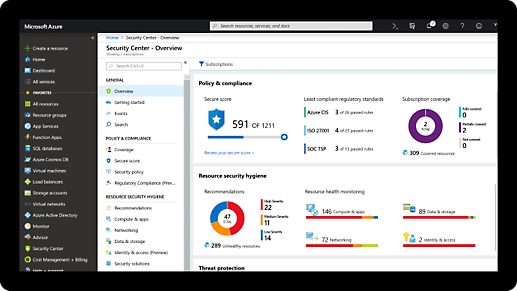
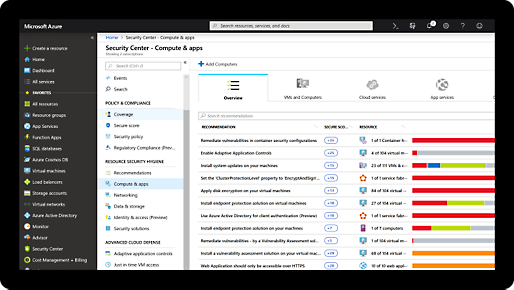
Comprehensive security and compliance, built in
-
We employ more than 8,500 security and threat intelligence experts across 77 countries.
-
Azure has one of the largest compliance certification portfolios in the industry.
-
Chaos Studio pricing
Chaos Studio is pay as you go based on experiment execution—chaos engineering experiments are charged per action-minute based or for the duration that your experiment actions run.
Get started with an Azure free account
1

2

After your credit, move to pay as you go to keep building with the same free services. Pay only if you use more than your free monthly amounts.
3

Chaos Studio resources and documentation
Get started with learning resources
Learn more about reliability
Frequently asked questions about Azure Chaos Studio
-
Chaos engineering is the practice of subjecting applications and services to real-world stresses and failures to build and validate resilience to unreliable conditions and missing dependencies.
-
-
Chaos Studio has a growing library of faults.
View the current list.
-
Chaos experiments require explicit granular permission to inject faults against resources.