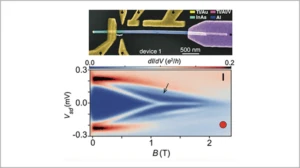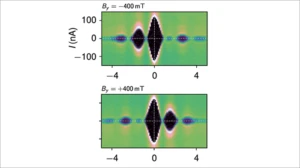
Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks
Working together, ETH Zurich and Microsoft QuArC researchers have provided the first application of machine-learning techniques to solve outstanding problems in quantum physics. The neural networks used in their study developed a genuine intuition of the bizarre behavior of quantum particles.