Azure Orbital Ground Station, Networking, Thought leadership
Deepen the value chain for geospatial earth imagery on cloud using Azure Orbital
Posted on
3 min read
Azure Orbital, a managed ground station service, enables customers to communicate to, control their satellite, process data, and scale operations directly in Microsoft Azure. Since our Azure Orbital announcement, we have been rapidly building and deploying ground stations in our datacenters. We are currently deploying multiple satellite ground stations in our datacenters that enable a variety of scenarios, including Earth Observation, Remote Sensing, and Global Communications.
Azure Orbital ground station update
With Azure Orbital, we are building satellite ground stations in our datacenters, allowing customers to ingest data from their satellites directly in Azure for processing and storage at-scale. Below is a sneak peek of our first satellite ground station in our Quincy, Washington datacenter:

We continue to build ground stations in other locations and integrate with partner ground stations to further our customers’ ability to communicate with their satellites for data ingestion.
In collaboration with several customers and partners, we have created multiple scenarios for signal processing, data processing, and geospatial data analytics. Today, we are pleased to welcome another partner into our Orbital ecosystem—Thales Alenia Space (TAS). TAS’s Deeper Vision and Microsoft’s Azure Orbital will bring great data processing, inferencing, and analytics capabilities to our customers.
Thales Alenia Space partnership
Together with Thales Alenia Space, we are bringing near real-time geospatial data processing capabilities to our customers. The power of processing data on the cloud with Azure Orbital coupled with the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technology helps our customers analyze environmental changes captured with satellite imagery.
Drawing on over 40 years of experience and a unique combination of skills, expertise, and cultures, Thales Alenia Space, a Joint Venture between Thales (67 percent) and Leonardo (33 percent), delivers cost-effective solutions for telecommunications, navigation, Earth observation, environmental management, exploration, science, and orbital infrastructures. Governments, institutions, space agencies, and telecom operators count on Thales Alenia Space to design satellite-based systems that provide anytime, anywhere connections and positioning, monitor our planet, enhance management of its resources, and explore our Solar System and beyond.
“Thales Alenia Space and Microsoft are innovating together by combining their expertise in space and cloud technologies. Customers can now combine all the functionality of Thales Alenia Space’s DeeperVision solution for processing dataflows and generating timely information with the cloud capabilities of Azure Orbital. This information is enriched by high-speed, high-volume artificial intelligence and machine learning to create an unprecedented impact on and beyond the planet!” – Clarence Duflocq, Vice President Strategy & Innovation, Thales Alenia Space
Use case: Geospatial data value-chain
Customers can use Azure Orbital and Orbital ground stations to bring geospatial data from their satellites. The raw satellite data can then be processed at-scale on the cloud for analysis using various Azure services to achieve goals like Change Detection, Site Monitoring, Situational Awareness, and Entity Recognition.

Deeper Vision performs automated content extraction from images and enriches image data. The user can request images from specified content, which will prompt Deeper Vision’s automation and allow the user to focus on tasks where human expertise is critical. This ability becomes crucial for scenarios like change detection and site monitoring. When new imagery arrives from specific areas, Deeper Vision can compare it with previously acquired imagery to highlight places that changed.
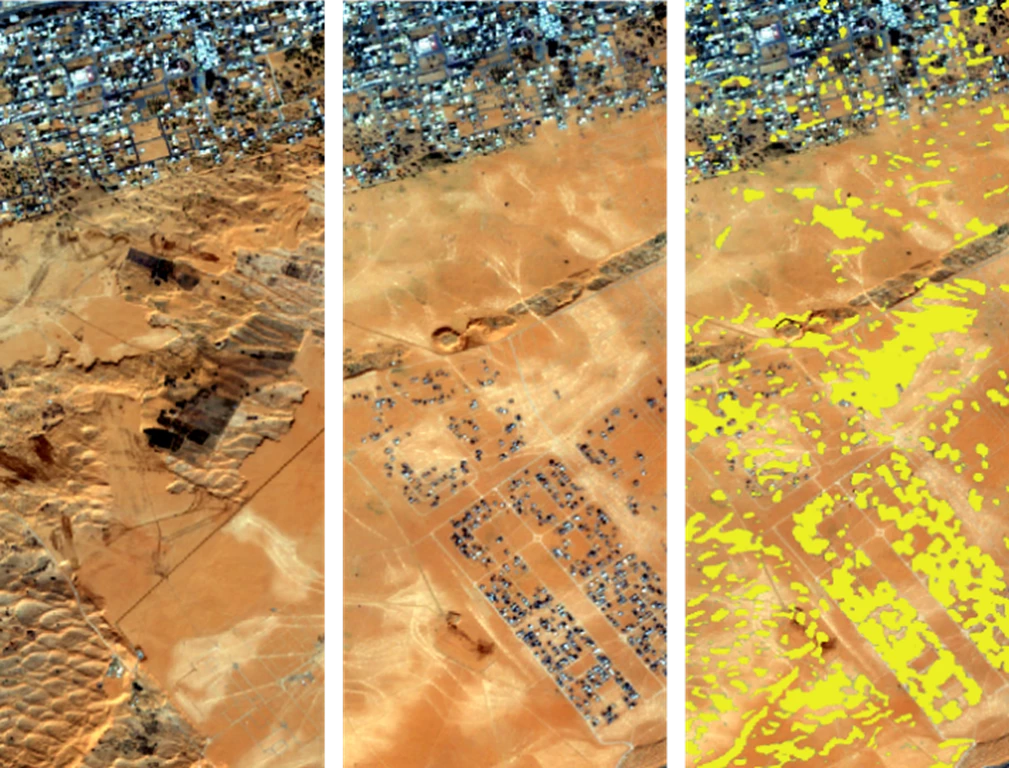

In the example above, we have two images taken by the European Space Agency Satellite Sentinel 2—one from 2016 and one from 2018. We can see that volumes of earth have been removed from the desert, and a neighborhood has been built. The image on the far right highlights the change detected.
Demo: Deeper Vision and Azure Orbital
In three easy steps, geospatial data, downlinked using Azure Orbital, can be processed on the cloud in near real-time for business transformational insights:
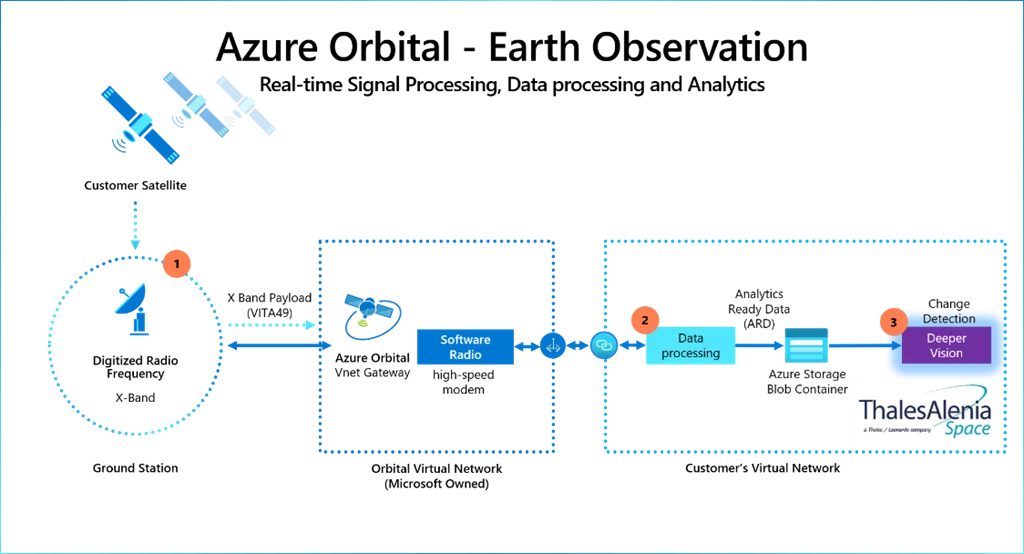
Step 1: The earth imagery is downlinked from a customer satellite. In September 2020, with a live downlink from AQUA, a public satellite owned and operated by NASA that stores downlinked data in an Azure Storage account, we demonstrated how customers can downlink data from the satellite using Azure Orbital.
Step 2: The satellite operator can process raw data from the Azure Storage Blob using their data processing pipeline for satellite imagery, which will convert them into final assets. If necessary, these assets can then be stored back in Azure Storage.
Step 3: With Deeper Vision, customers can perform inferencing on these geospatial images—a capability by our partner TAS that brings services like change detection and entity recognition.
Learn more
Deeper Vision and TAS are coming to Azure Marketplace soon. Find a demo of Azure Orbital and Deeper Vision in action.